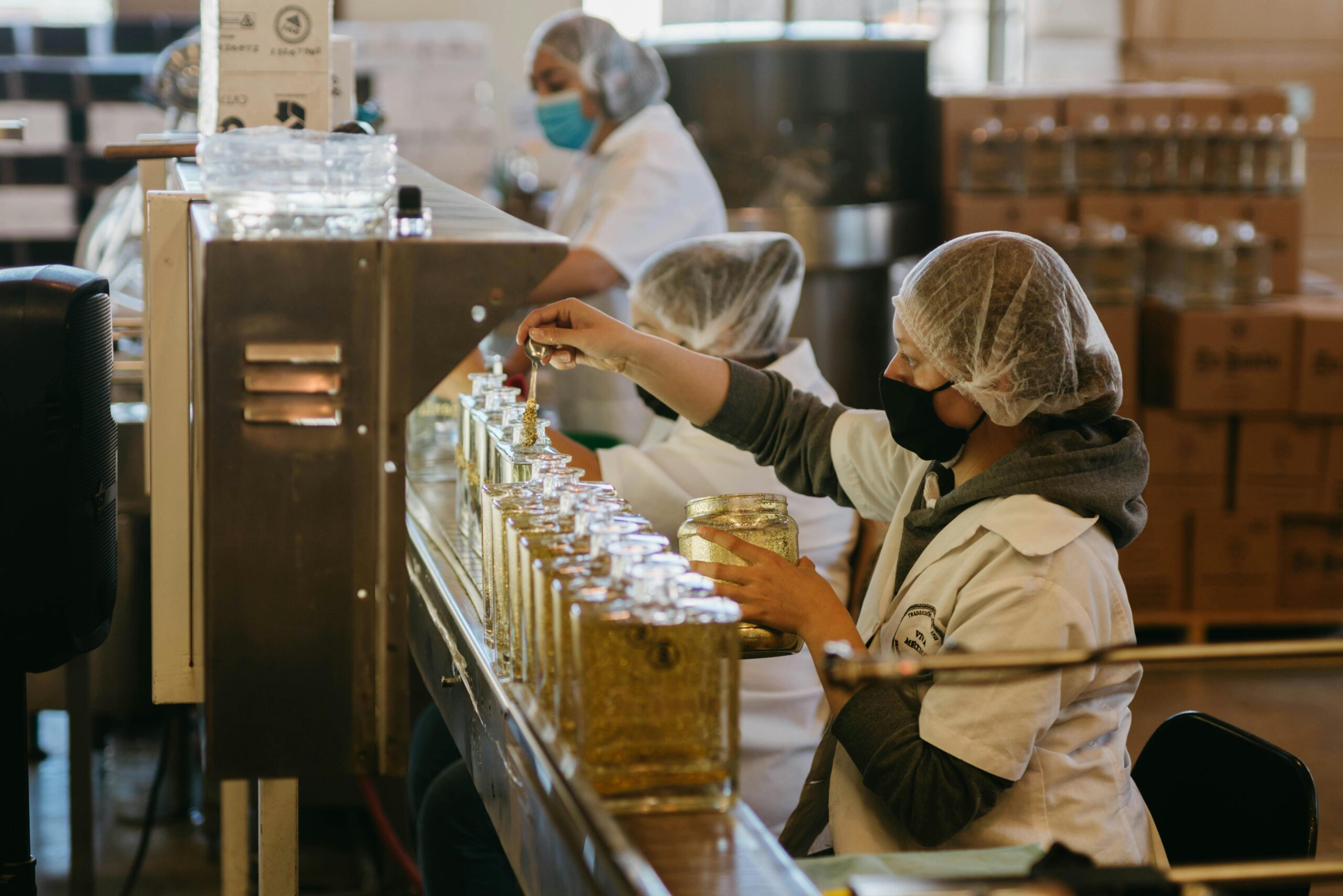
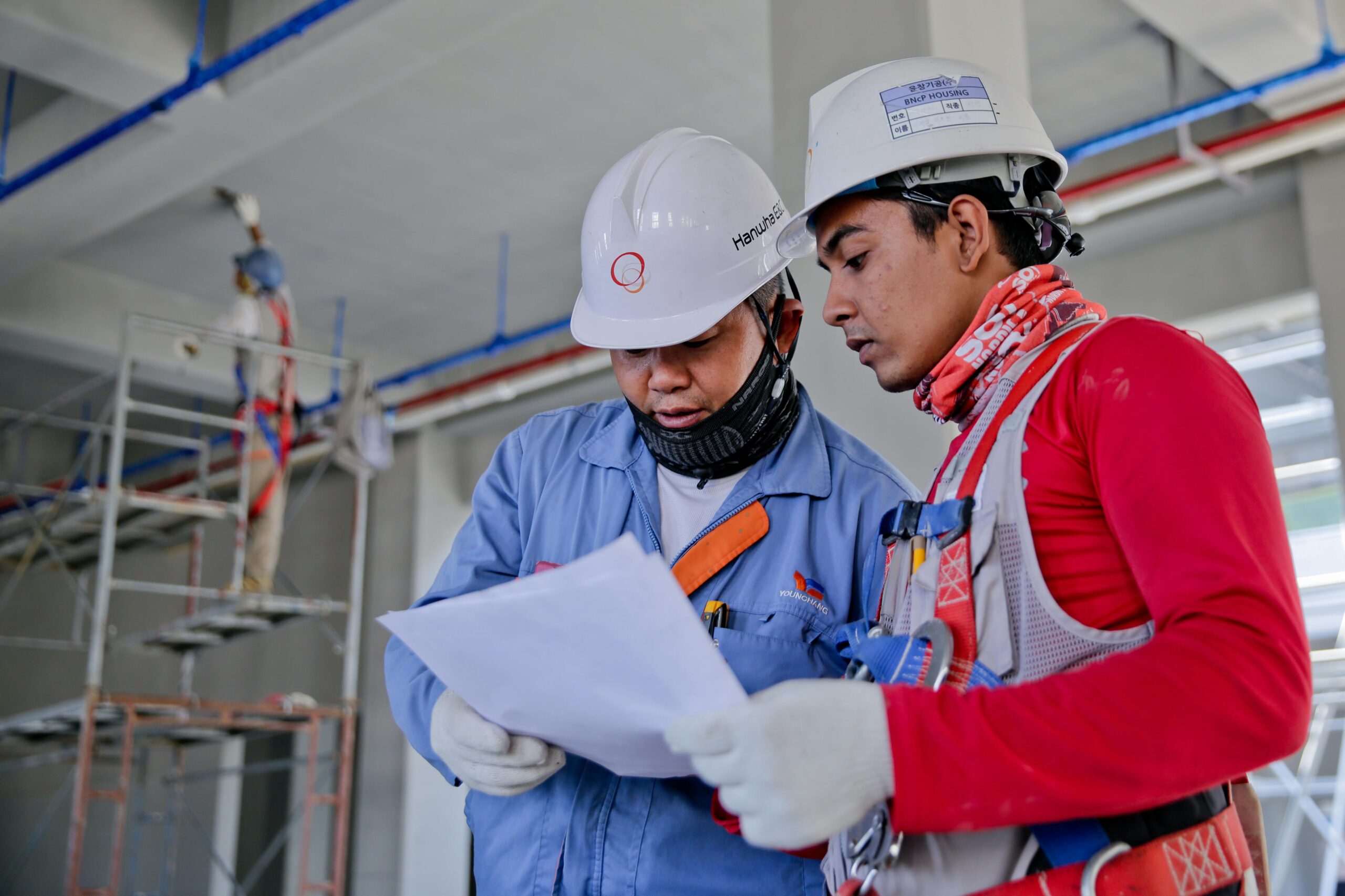
Quality Control (QC) refers to the processes that ensure products and services meet required quality standards. It also pushes the quality standards themselves to improve
Quality Control managemant
Quality Control (QC) refers to the processes that ensure products and services meet required quality standards. It also pushes the quality standards themselves to improve. It involves the systematic inspection, testing, and verification of various aspects of a product or service before it is delivered to the customer. The primary objective of quality control is to identify and correct defects or variances in the production process that could lead to a substandard product, thereby preventing errors from reaching the final consumer.
The various quality control processes and practices help to maintain a certain level of excellence. Here’s how it works:
1.Establishing Quality Standards
The first step is to define specific standards that products or services must meet. These standards are based on customer requirements, industry regulations, and the company’s benchmarks for quality. These standards should be well-documented and easy to understand. It’s important to set key performance indicators (KPIs) for factors like: reliability, durability, accuracy, safety, and performance.


- Setting Acceptance Criteria
Next, it is important to set the acceptance criteria, which are the specific conditions under which a product is considered to have met the quality standards. These criteria make the quality standards measurable and enforceable. For example, for a software development team, this could be software with bug-free functionality.
- Implementing Quality Control Measures
At this stage, specific measures and procedures are put in place to ensure that the production process adheres to the established standards. This can include the use of: specialized equipment, quality control checklists, and standardized practices.
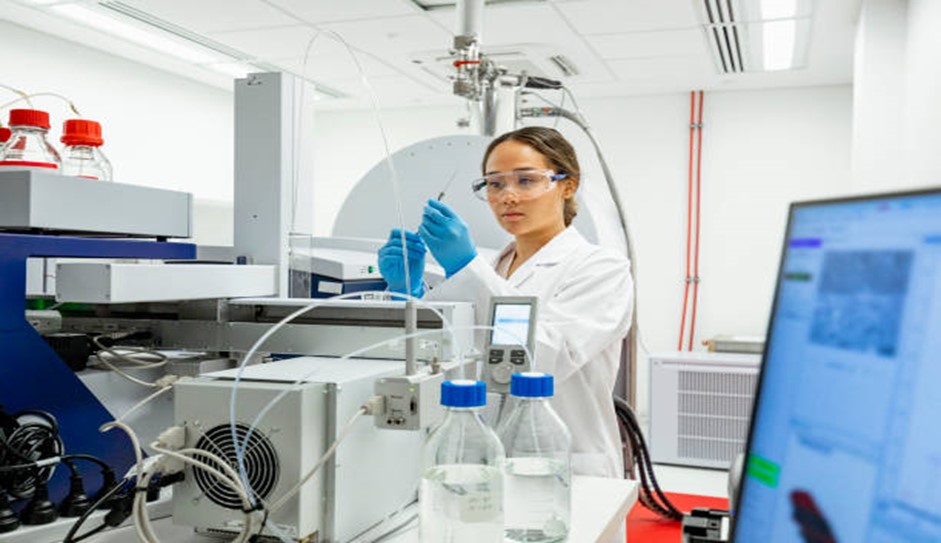


- Monitoring Process Performance
Continuous monitoring of the production or service delivery process is essential to identify any deviations from the quality standards. This means regular inspections, testing, and analysis to detect deviations from the desired quality parameters.
- Identifying Defects and Non-Conformities
When monitoring reveals defects or non-conformities, these issues must be documented and analyzed. Naturally, the problems must be identified before any corrective action is possible.

- Root Cause Analysis
Any time defects or non-conformities are identified, a root cause analysis is conducted to determine why the issues occurred. This analysis is critical for addressing the underlying problems and preventing future defects.
- Implementing Corrective Actions
Based on the findings from the root cause analysis, corrective actions are taken to rectify the identified issues. This may involve revising procedures, retraining staff, or making changes to equipment or materials.


- Continuous Improvement
Quality control is an ongoing process that seeks to continuously improve the quality of products and services. Organizations can enhance efficiency, reduce waste, and improve customer satisfaction by regularly reviewing and refining QC processes.
- Supplier Quality Management
Quality control extends to managing the quality of materials and components obtained from suppliers. This means assessing supplier capabilities, conducting audits, and establishing quality agreements to ensure that all inputs meet the standards.


- Documentation and Record Keeping
Effective quality control requires proper documentation and record-keeping. All records of inspections, tests, defects, corrective actions, and improvements must be retained and cataloged. Documentation provides a traceable history of quality and is essential for compliance, analysis, and continuous improvement efforts.
- Invest in Employee Training
Provide ongoing training to equip employees with the necessary skills and knowledge to maintain high-quality standards.


Benefits of Quality Control for Manufacturing Businesses
- Customer Satisfaction: The Ultimate Goal
- Cost Savings Through Error Prevention
- Streamlining Processes for Enhanced Efficiency
- Waste Reduction and Sustainability
- Enhanced Brand Reputation
- Compliance with Industry Regulations
- Technological Advancements and Innovation
- Proactive Issue Resolution
- Employee Morale and Engagement
- Future-Proofing the Business





