Lean Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing also called lean Production, is as a set of tools and methodologies that aims for the continuous elimination of all waste in the production process. The main benefits of this are lower production cost, increased output and shorter production lead times.
Employees become more engaged in the manufacturing process, sharing ideas, leading improvements and driving positive change in all departments.
Information management becomes more simpler and more accurate.
Information displayed will highlight improvement opportunities, be relevant and understandable, and recognise and celebrate success.
The ultimate goal is to provide a perfect product to the customer through a perfect value creation process that has zero waste
Principal of Lean Manufacturing
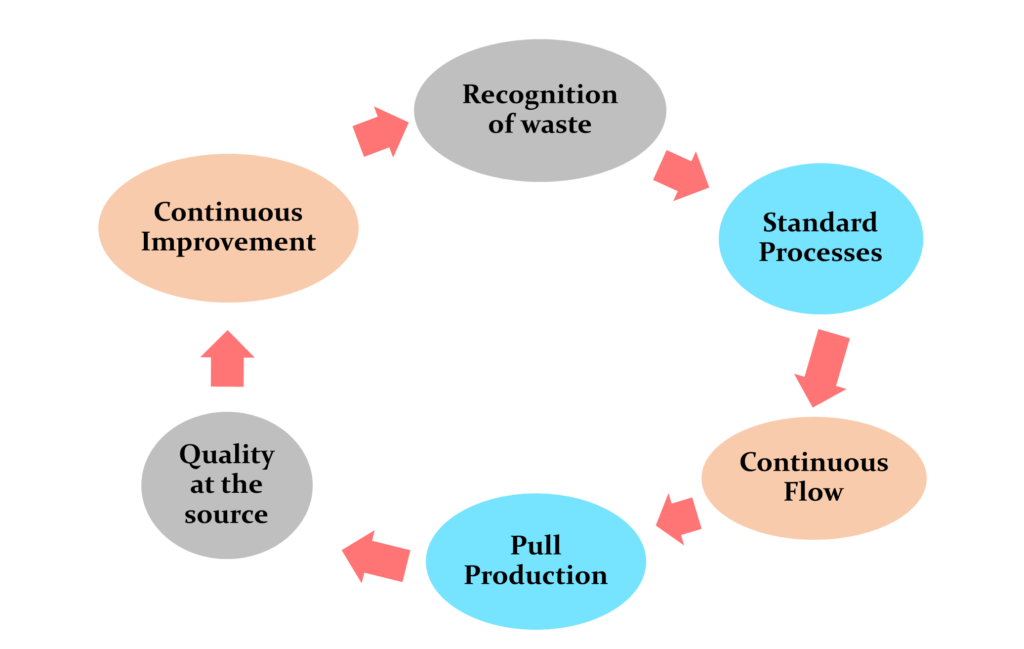
Lean Tools
Standard Work
Standard work means that the production process and guidelines are very clearly defined and communicated, in a high level of detail, so as to eliminate variation and incorrect assumption’s in the way that work is performed.
The goal is that production operations should be performed the same way every time, unless the production process is intentionally modified.


Visual Management
Simple signals that provide an immediate understanding of a situation or condition.
A good rule of thumb is that anybody should be able to walk into a department and within two minutes, be able to understand the basic process and controls in place. This can be achieved using colour coding, systematic production layout pictures, signs and floor marking.
Bottleneck Analysis
Identify which part of the manufacturing process limits the overall throughput and improve the performance of that part of the process.

Continuous Flow
Manufacturing where work-in-progress smoothly flows through production with minimal (or no) buffers between steps of the manufacturing process
Gemba
A philosophy the reminds us to get out of our office and spend time on the plant floor – the place where real action occurs.


Heijunka
A form of production scheduling that purposely manufactures in much smaller batches by sequencing(mixing) product variants within the same process.
Jidoka
Design equipment to partially automate the manufacturing process ( partial automation is typically much less expensive then full automation) and to automatically stop when defects are detected.


Jit ( Just In Time )
Pull parts through production based on customer demand instead of pushing parts through production based on projected demand. Produced and convey what customers want, when they want in exactly the amount they want.
Kaizen
A strategy where employee work together proactively to achieve regular, incremental improvements in the manufacturing process.
Kai+Zen = Better + Change


OEE( Over All Equipment effectiveness)
Framework for measuring productivity loss for a given manufacturing process. Three categories of loss are tracked
- Availability (e.g. down time)
- Performance (e.g. slow cycles)
- Quality (e.g. reject )





